Term Used to Describe Glucose Attached to Hemoglobin
The A1c is just a fancy way of saying the hemoglobin has a sugar molecule attached to it and what that hemoglobin A1c. Carbonyl group attached to the center carbon atom making it a ketone.
Glycosylated Hemoglobin Test Western New York Urology Associates Llc
Initially an unstable bond is formed between glucose and the hemoglobin molecule.

. Glycosylated hemoglobin is tested to monitor the long-term control of diabetes mellitus. The level of glycosylated hemoglobin is increased in the red blood cells of persons with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus. So these red blood cells that are called freely permeable to glucose.
The more glucose in your blood the more it sticks. When you have glucose in your blood it glycates sticks to hemoglobin. Glycosylated hemoglobin is tested to monitor the long-term control of diabetes mellitus.
What term is used to describe an excess of glucose in a urine sample. A1C is a type of hemoglobin formed by attachment of glucose to the hemoglobin. GHb is a general term used to describe hemoglobin that has been modified by addition of glucose through a nonenzymatic process.
An HbA1c test shows what the average amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin has been over the past three months. The test is based on the fact that glucose enters red blood cells and becomes irreversibly attached to hemoglobin within the cells. Glycated hemoglobin glycosylated hemoglobin any of various hemoglobins with glucose attached nonenzymatically.
Hemoglobin to which glucose is bound. The term used to describe the volume of air exchanged during normal inspiration and expiration is. A1C test is a test which measures how much of your hemoglobin has got attached to glucose and reflects the level of blood glucose in a person over the past 3 months.
The A1c test measures the average amount of glucose thats been attached to hemoglobin over time. Medical Definition of Glycosylated hemoglobin Definition of Glycosylated hemoglobin Glycosylated hemoglobin. Hemoglobin haemoglobin BrE from the Greek word αἷμα haîma blood Latin globus ball sphere -in ˌhiːməˈɡloʊbɪn ˈhɛmoʊˌ- abbreviated Hb or Hgb is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in red blood cells erythrocytes of almost all vertebrates the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae as well as the tissues of some invertebrates.
It cant un-attach to hemoglobin. Evaluates the average blood glucose control over 3 4 months Glycogen Glucose is stored in your body in the form called glycogen. When you take two monosaccharides and dehydrate them it will attach with an oxygen molecule forming what.
The HbA1c sub-type reacts irreversibly. A hemoglobin A1c HbA1c test measures the amount of blood sugar glucose attached to hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the substance in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the cells.
During its 120-day life span in the red blood cell hemoglobin becomes glycosylated to form HbA1. A measurement between 140-199 mgdL indicates prediabetes and a reading of 200 mgdL or greater after. As a persons blood sugar becomes higher more of the persons hemoglobin becomes glycosylated.
In this case a blood sugar level of less than 140 mgdL after two hours means youre fine. The rate at which glucose binds to hemoglobin is dependent on the blood glucose concentration. Since blood cells live about 90 days or so the amount of HbA1c present at any time is a record of how much glucose has been in the blood during that period.
The most common one is hemoglobin A 1c. The term prediabetes is often used to describe a situation where the blood sugar level is higher than normal but. Not a term recognized by the American Diabetes Association borderline diabetes is sometimes used to describe prediabetes.
Glucose a type of sugar molecules in the blood normally become stuck to hemoglobin molecules - this means the hemoglobin has become glycosylated also referred to as hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c. Term used to describe the formation of a hemoglobin compound produced when glucose reacts with amino group of Hgb a protein. Most methods quantify HbA 1c defined as HbA with glucose attached to the NH 2-terminal.
A drop in the bodys production of carbonic anhydrase would hinder the formation of. Which means that glucose thats floating in your blood can get right in the red blood cell. One such thing is extra glucose so if you have too much glucose circulating in your blood the glucose will essentially bind on to a little hemoglobin pocket and we call that glucose containing hemoglobin hemoglobin A1c.
About 985 of the oxygen carried by systemic arterial blood is attached to. The glucose molecule attaches non-enzymatically to the hemoglobin molecule in a ketoamine structure to form a ketoamine. Glycosylated HemoglobinGlycosylated hemoglobin hemoglobin A1C HbA1C and A1C are terms used to describe hemoglobin into which glucose has been incorporated.
Individuals with sickle cell trait have inherited only one copy of the gene for sickle cell hemoglobin and one for normal hemoglobin. Glycohemoglobin also known as glycosylated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A 1 C is a hemoglobin-glucose combination formed nonenzymatically within the cell. Brittle diabetes A term not recognized by the American Diabetes Association sometimes used to describe when a persons blood sugar blood glucose levels move in extremes from low to high and from high to low.
Hemoglobin is the part of your red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. Hemoglobin normally does not contain glucose when it is released from the bone marrow. Hemoglobin reacts with blood glucose in various ways.
Glycosylated hemoglobin is the term used to describe the formation of a hemoglobin compound formed when glucose a reducing sugar reacts with the amino group of hemoglobin a protein. Glycated hemoglobin test HbA1c Blood test that measures glucose attached to red blood cells. Term used to describe how easily a cell can react with insulin Juvenile onset Old name for type 1 diabetes.
And it can stay there for around three months or about how long the average red blood cell lives. Hemoglobin to which glucose is bound. And as soon as it does it basically attaches to hemoglobin and then as soon as it attaches to hemoglobin thats it.
Plasma protein ketoamines reflection of short term glucose control 3-6 weeks.

Schematic Illustration Of The Formation Of Glycated Hemoglobin Hba1c Download Scientific Diagram

Hemoglobin A1c The Three Month Test

Pathologists Lancet Kenya Hemoglobin A1c Also Called A1c Or Glycated Hemoglobin Is Hemoglobin With Glucose Attached The A1c Test Evaluates The Average Amount Of Glucose In The Blood Over The Last
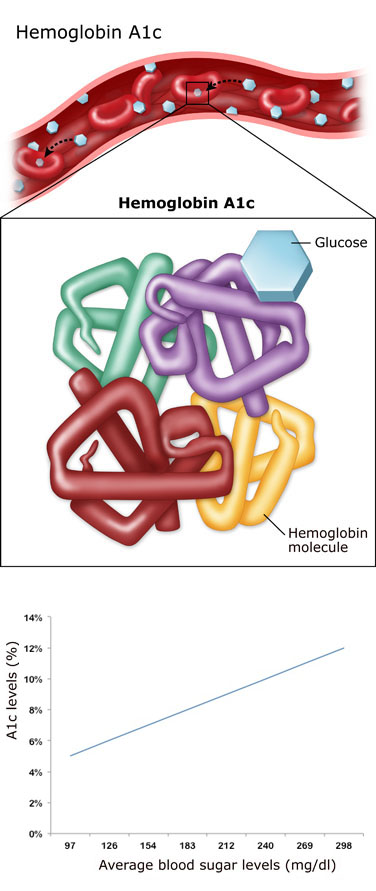
Understanding Your Average Blood Sugar Diabetes Education Online
Comments
Post a Comment